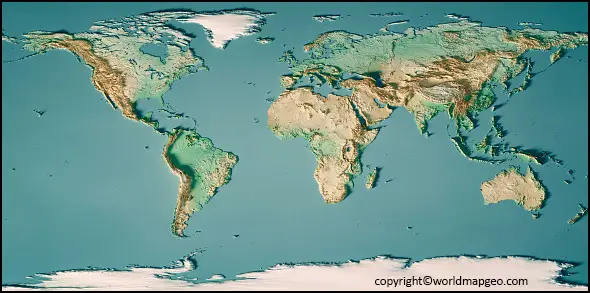
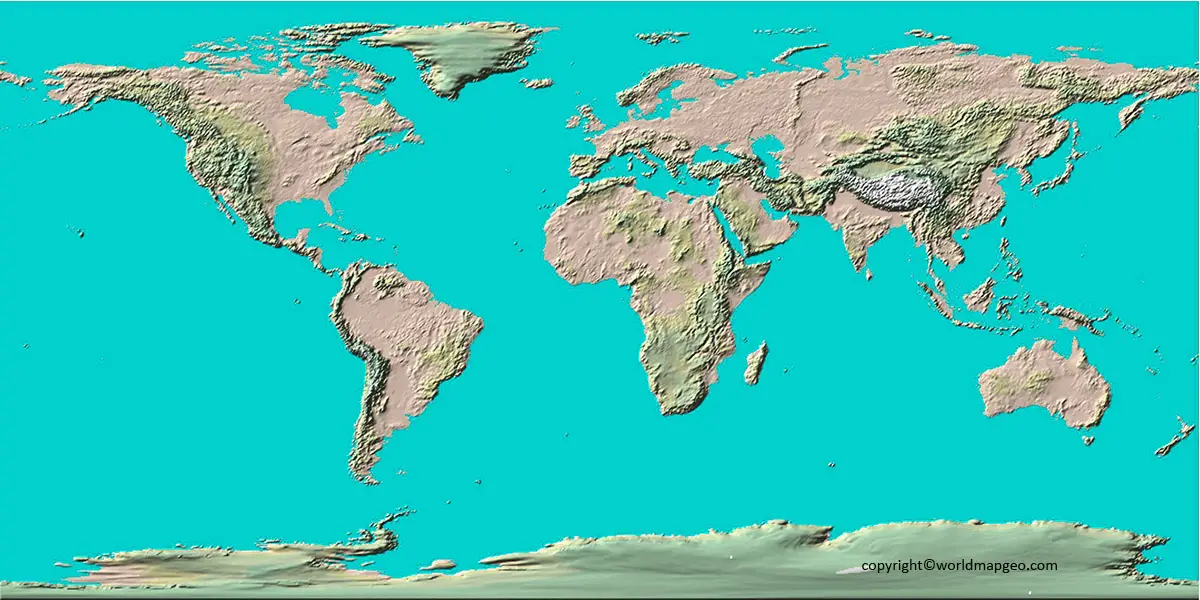
A World Topographic Map depicts manufactured and natural elements on the ground, such as roads, trains, electricity transmission lines, contours, altitudes, rivers, lakes, and geographical names, in great detail and accuracy. The topographic map depicts the three-dimensional geography of the Earth in two dimensions. The scale of the most often used Canadian topographic map is 1:50 000.
This topographic map shows where geographical features are located. Examples are mountains, valleys, plains terrain, water bodies, and other geographical features. Topographic maps are large and medium-scale maps that contain a tremendous amount of information. Therefore, each component of a topographic map is equally important. Also, you can check out the other world maps here for free with their image and PDF format such as:
- Blank World Map
- World Map Physical
- World Map with Continents
- Political World Map
- World Map with Equator
- World Time Zone Map
- Printable World Map
- World Map for Kids
- World River Map
World Topographic Map 3D
Numerous ground characteristics are identified on high-resolution world topographic map and can be classified as follows:
· Relief: Contours define mountains, valleys, slopes, and depressions.
· Hydrography: Lakes, rivers, streams, bogs, rapids, and falls are all examples of natural phenomena.
· Landscaping: forested areas
· Transportation: Airports/airfields, seaplane anchorages, roads, paths, railways, bridges
· Culture: Buildings, urban growth, transmission lines, pipelines, and towers are all examples of infrastructure.
· Boundaries: international, provincial/territorial, administrative, recreational, and geographical are all terms used to describe a situation.
· Toponymy: Boundary names, location names, water feature names.
Map of the World Topographic
All features and their accompanying symbols are shown in the map legend. The information along the map’s boundaries is helpful for understanding and using a topographic map. Here, for example, you’ll see the map scale and other pertinent details about the map, such as the year, edition, and data.
World Topographic Map Colors
They can depict the three-dimensional landscape in two dimensions, topographic maps are valuable tools. A topo map can locate peaks, valleys, ridges, and saddles, among other terrain features. Contour lines connect locations of equal elevation on a topo map, indicating height. Imagine traveling in a circle around a mountain, never going uphill or downwards, and staying at the same peak.
The contour lines’ shape might reveal the formation of a region’s landforms. Concentric circles, for example, depict a peak, with a minor process denoting the apex. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep terrain, while far apart contour lines suggest level terrain.
Labeled Topographic World Map
Topographic maps depict the Earth’s characteristics correctly and scale on a two-dimensional surface. Therefore, topographic maps are a great planning tool and guide that makes outdoor trips more pleasurable and safe. It has numerous applications, which are listed below:
· These maps can be used for any geographic or architectural planning.
· It has applications in Earth Science and Geography.
· It can be utilized in mining and other applications such as pond construction.
· This is also suitable for recreational uses. Hiking or mountaineering, for example.
· However, it can also obtain extensive information about any location or geographical feature. Drainage, landforms, forests, communication or transit lines, and so on are examples.
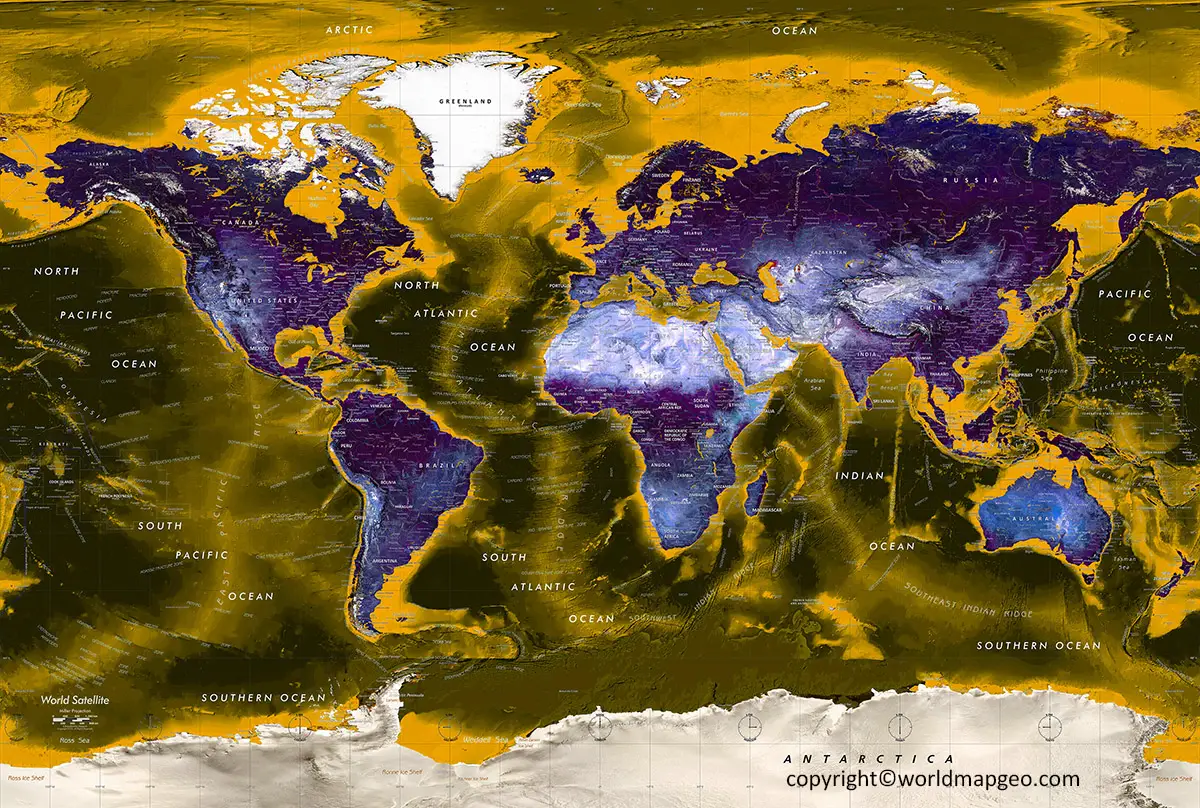
Interactive Topographic Map World
As you can see here Interactive World Topographic Map with its detail and Image and PDF format at the same time.
· It can also be utilized to obtain extensive information on any artificial features.
· It can also be applied to civil engineering.
· Altough, The government can utilize it for planning and administrative purposes, as well as by commercial industry actors.
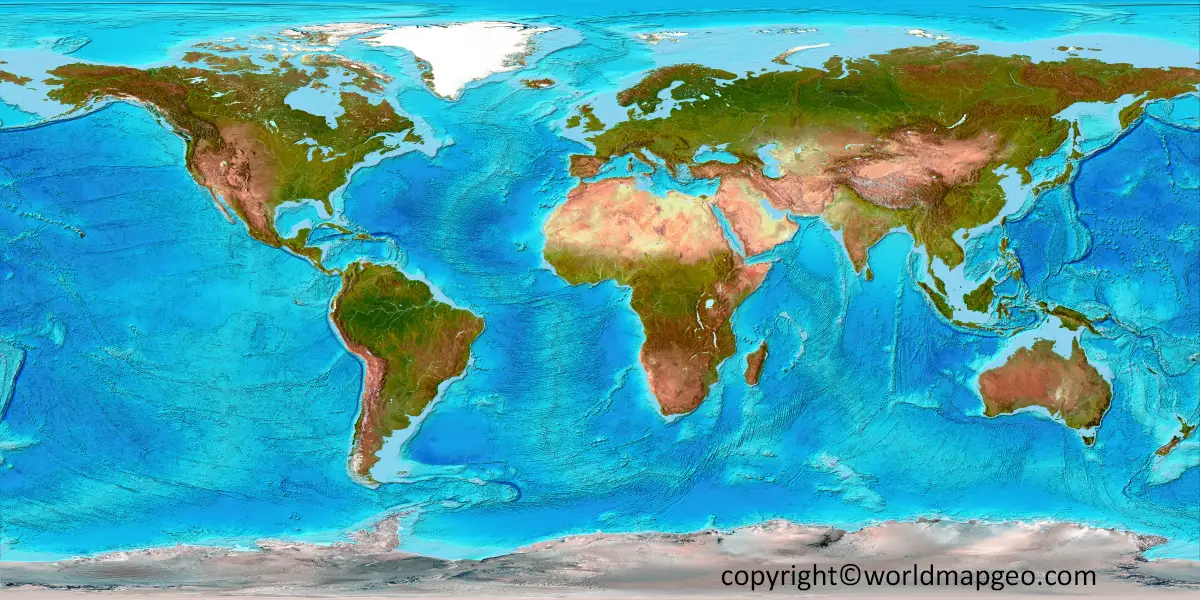
Topographical Map of The World
A topographical provides a detailed representation of the Earth’s physical features, including landforms, elevation, and terrain. It offers a unique perspective on the planet’s surface, showcasing the highs and lows of different regions. Here’s some information about a topographical map:
- Elevation and Contour Lines: A topographical map uses contour lines to indicate changes in elevation. These lines connect points of equal elevation above or below a reference point, such as sea level. Closer contour lines signify steep slopes, while widely spaced lines indicate gentle terrain. By following the contour lines, users can visualize the shape of mountains, valleys, plateaus, and other landforms.
- Landforms and Features: A topographical map showcases various landforms and features that shape the Earth’s surface. These can include mountains, hills, valleys, plains, deserts, forests, rivers, lakes, and coastlines. The map highlights the diversity and distribution of these features worldwide, allowing users to explore the geographical characteristics of different regions.
- Relief and Shading: To provide a sense of three-dimensionality, topographical maps often use shading or color to represent different elevations. Lighter colors or shading indicate higher elevations, while darker colors represent lower elevations. This technique helps visualize the relief and terrain variations across the world, giving a sense of depth and perspective.
- Mountain Ranges and Volcanoes: Topographical maps prominently display major mountain ranges and volcanoes, which are significant features of the Earth’s topography. Users can identify iconic ranges like the Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, or Alps, as well as individual peaks and volcanic formations. The map allows for an appreciation of the magnitude and distribution of these geological formations.
- Oceans and Seas: While the focus of a topographical map is primarily on landforms, it may also include underwater topography, such as oceanic ridges, trenches, and seamounts. These features provide insights into the topography of the ocean floor and its geological characteristics.
- Scale and Legend: Topographical maps provide a scale bar to indicate the relationship between map distance and real-world distance. The scale helps users understand the relative sizes of landforms and features. Additionally, a legend is included to explain the symbols and colors used on the map, enabling users to interpret the information correctly.
- Practical Applications: Topographical maps serve various practical applications. They are vital tools for outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, mountaineers, and adventurers who rely on accurate information about terrain and elevation. They are also valuable for urban planning, environmental management, and scientific research, providing insights into the Earth’s physical characteristics and landforms.
In conclusion, a topographical map offers a detailed depiction of the Earth’s surface, emphasizing landforms, elevation, and terrain. It provides a unique perspective on the planet’s topography, allowing users to explore and understand the diverse physical features that shape different regions. Whether used for outdoor activities, research, or planning, a topographical map offers a wealth of information about the Earth’s natural landscape.